Your Reliable Partner
Chip Resistor Guide: What It Is and How It Works
With the rapid growth of electronic devices, the demand for reliable circuit protection components like chip resistors has surged. Engineered for optimal performance in harsh environments, chip resistors are essential across industries, from consumer electronics to automotive and industrial sectors.
This article explores their fundamentals, classifications, and how they work—equipping you with the knowledge to make informed design decisions.
Chip Resistor Basics: Ensure Circuit Accuracy with the Right Choice
Chip resistors regulate current flow in circuits and exist as compact, passive electronic components. These small, flat, rectangular circuit protection components resemble tiny chips.
Manufacturers produce them by mixing metal and vitreous enamel powders and applying the mixture to substrates via screen-printing. They add metallised ends on each side to enable easy placement and connection on circuit boards.
Engineers use chip resistors to operate, protect, and control circuits while reducing voltage or current signals. Chip resistors cannot increase voltage or current. Without resistors, excessive current flow would damage electronic devices.
Chip resistors oppose DC and AC current flow, applying resistivity principles and Ohm’s law. Manufacturers achieve desired resistance values by combining metal alloys with different conductivity levels.
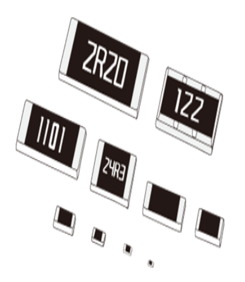

Selecting the Right Chip Resistor: A Guide to Types and Their Applications
Chip resistors can be classified according to their construction type, circuit function and termination lead. Let’s walk through some of the common classifications of these circuit protection components:
Construction Type
- Fixed resistors: These compact, rectangular components provide a set, predetermined resistance value for consistent circuit performance.
- Variable resistors: These allow you to adjust the resistance level to meet specific requirements, offering greater flexibility in circuit tuning.
- Non-linear resistors: These resistive components exhibit non-linear behaviour when it comes to temperature and voltage.
Circuit Function for Applications
- Voltage dividers: These simple and passive linear circuits can turn a larger voltage into a smaller one.
- Current limiting: This is a protective resistor that prevents appliances from exceeding the current limit.
- Shunt measure: These resistors are used to measure current flow by producing a voltage drop proportional to the current.
- Heaters: Designed for heating applications, these resistors convert electrical energy into heat.
- Strain gauge: Commonly used in sensors and transducers, these resistors detect mechanical strain and deformation in materials.
Termination Lead Types
- Through-hole: These resistors feature two wire terminals that engineers insert and solder onto a printed circuit board (PCB) to oppose current flow.
- Surface Mount Devices (SMD): Surface mount resistors are small rectangular components that use surface-mount technology to save space compared to conventional resistors.
- Chassis: These large resistors adjust parameters such as signal levels, biasing of active elements, and other circuit requirements.
- MELF: Engineers consider these among the most stable and reliable resistors, performing better than SMDs and meeting demanding automotive industry requirements.
Now that you have a good idea about the different classifications of chip resistors, let’s explore some of the most widely used technologies in chip resistors:
Thin Film Technology
Thick Film Resistors
Foil Resitors
Manufacturers construct thin film resistors by depositing a thin metallic coating onto a ceramic substrate.
These resistors provide high resistance per area and deliver enhanced precision and stability across varying temperature ranges.
Manufacturers create these by stencilling a resistive metallic paste onto the base.
Although thick film resistors produce more noise, they offer a cost-effective solution for general-purpose applications.
Manufacturers apply a metal foil to a ceramic substrate and photo-etch it with a resistive design to create foil resistors.
These resistors offer benefits such as non-inductance, enhanced stability, and reduced capacitance and noise, making them a popular choice.
Finding the Right Type of Chip Resistor: Factors to Consider Before You Make Your Purchase
With a multitude of applications in electronic circuits, it is essential to gauge the necessary operating parameters for your specific design when selecting chip resistors. Here is an easy guide to make your life easier:
Determine the Required Distance
The chip resistor you choose must meet the required resistance value for your application
Gauge Size Constraints
When selecting chip resistors, the board space must also be taken into consideration; smaller resistors are typically required for high-density layouts, whereas larger resistors will be needed if you need to handle high power dissipation.
Identify the adequate power rating
Insufficient power rating can result in failure or damage; therefore, it is crucial to pick a chip resistor with the appropriate wattage.
Check the voltage rating
Ensure that the voltage value is higher than the maximum voltage, including transients. This is generally considered safer. Moreover, it is better to connect a series of resistors rather than using a single resistor at a higher voltage rating.
Verify the temperature coefficient
Make sure to check the operating temperature range before you make your purchase. A lower temperature can enhance stability, which is important for precision and reliability, especially over a wide temperature range.
Finding the Right Type of Chip Resistor: Factors to Consider Before You Make Your Purchase
As an industry leader in providing passive electronic devices, YAGEO’s products come with state-of-the-art technology and are of excellent quality. Here are some of their specifications and characteristics:
- Compact and lightweight
- Automated pick and place assembly
- High reliability and mechanical strength
- Enhanced precision with low inductance
- High power density with low capacitance
- Stable electrical performance
- Wide range of resistance values
- Withstands certain extreme environmental conditions
- Compliant with RoHS regulations
Why Choose Acton as Your Chip Resistor Distributor
Acton Technology is the authorized distributor of high-quality chip resistors for precision electronics manufacturing. We offer a complete selection of resistor types, including thick film, thin film, and specialty resistors, sourced from globally recognized manufacturers. Our supply is backed by dependable delivery, responsive customer service, and expert technical guidance tailored to your project requirements.
Moreover, when tight tolerances, high reliability, or urgent procurement are critical, project managers, R&D engineers, and sourcing teams rely on Acton to deliver the right chip resistors on time and to exact specifications.
For sourcing or technical assistance, contact us at contact@acton-tech.com.



