Thermal Interface Material: Efficient Heat Transfer Solutions
You’re an electrical/electronics design engineer working on power supply designs, you are familiar with the importance of thermal management on your system.
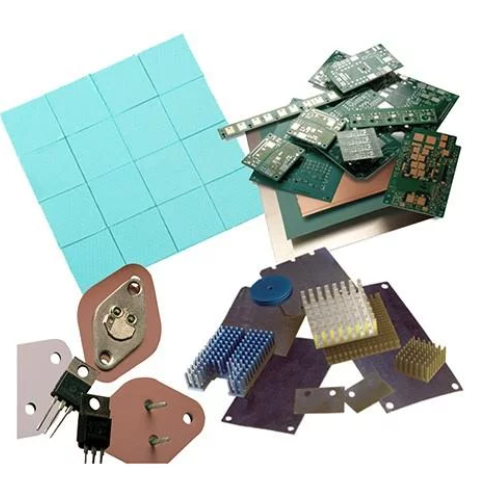
With power design trends getting more denser, keeping power components performing at optimal conditions by proper heat dissipation is a huge challenge. Thermal interface materials are supposed to help, but you’ve seen uneven performance.
Don’t tear your hair out yet! We’ll look at optimizing the thermal performance of your power components.
By the end, you’ll have new strategies for managing heat and keeping your designs cool.
Understanding Thermal Challenges in Power Supply Design
In power supply design, thermal management is absolutely critical to ensure safety, reliability and performance.
Heat Caused by Power Conversion
When AC power is converted to DC, a lot of heat is generated because of this conversion. The more power your supply handles, the more heat it produces.
If not properly dissipated, this heat can damage components and shorten the lifespan of your power supply.

Insufficient Cooling
If your power supply’s cooling system can’t keep up with the heat generated during operation, overheating will occur and worst case – thermal runaway. You’ll need to determine the maximum thermal load your supply can handle and ensure your cooling solution, like fans or heat sinks, can keep temperatures in the safe range.
Thermal Interface Materials
To transfer heat away from sensitive components, you need a material that conducts heat well and fills in air gaps. Thermal interface materials, like thermal pads or thermal grease, improve contact between surfaces and facilitate heat transfer.
Using a high-quality thermal interface material tailored to your needs can make a big difference in your power supply’s thermal performance and reliability. Acton Technology can provide you a range of thermal interface materials to suit your specific requirements.
With the right thermal management strategy and components in place, you’ll be well on your way to designing a power supply that delivers high performance and long life. Controlling heat is the key to success.
Key Sources of Heat in Power Supplies
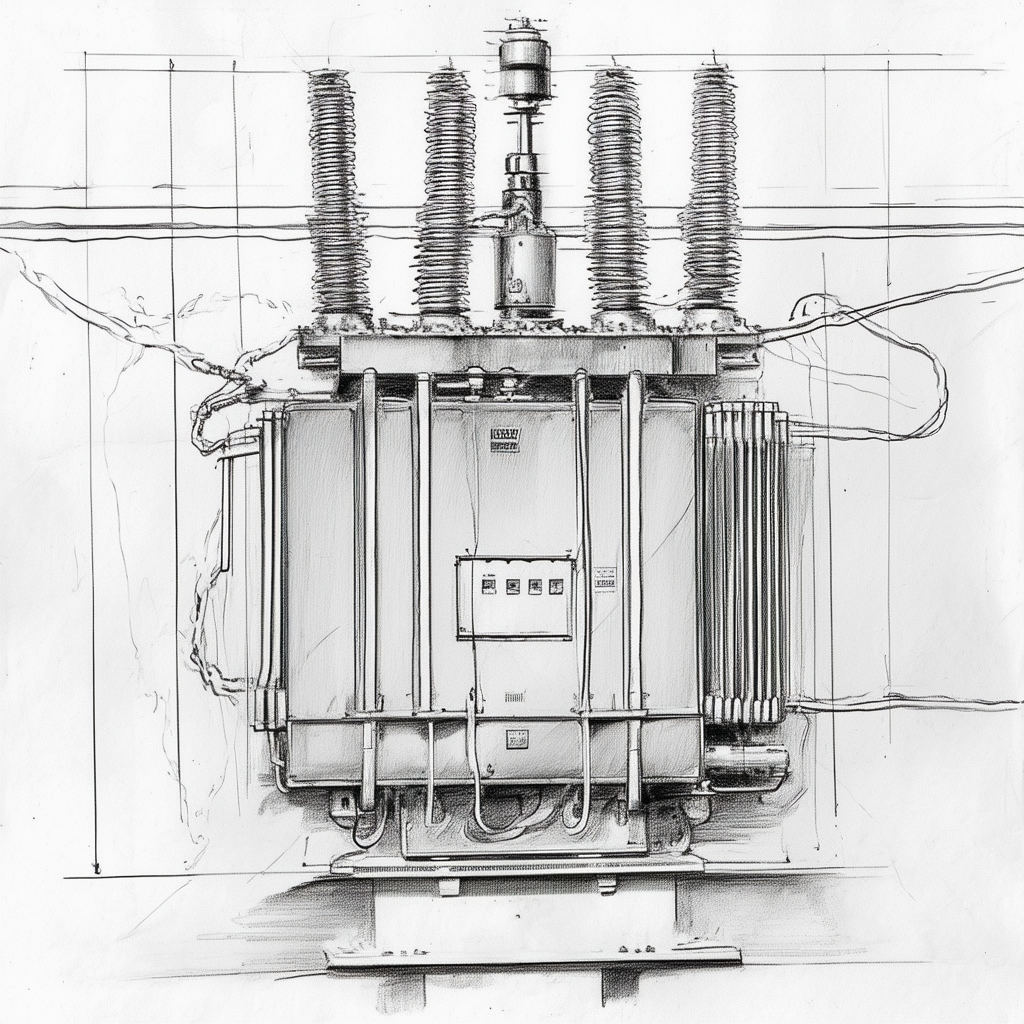
There are several components in power supplies responsible for generating heat. The first is the transformer, which steps down the AC line voltage to a lower DC output voltage. As current flows through the transformer coils, heat is produced due to electrical resistance.
Rectifier diodes are another source of heat generation. As AC is converted to DC, diodes allow current to flow in only one direction. However, some power is lost as heat during each rectification cycle.
Switching transistors or MOSFETs also generate heat as they rapidly turn on and off to regulate the output voltage. The higher the switching frequency or the higher is the current, the more heat is produced.
Capacitors store energy and release it when needed, but they are not 100% efficient. Some energy is lost as heat, especially for high-capacitance, high-ripple applications.
Thermal Management Solutions
To prevent overheating, power supplies require effective thermal management solutions. Heat sinks, fans, and thermal interface materials (TIMs) help dissipate and transfer heat away from critical components.
Heat sinks provide a large surface area to radiate heat into the surrounding air. Fans actively move the heated air away from components and out of the power supply enclosure. TIMs fill in air gaps between components and heat sinks to facilitate the transfer of heat.
Materials like silicone pads, greases, and solders improve contact and heat flow between uneven surfaces. For high-power applications, more advanced TIMs made of pyrolytic graphite or boron nitride nanosheets and with higher thermal conductivity can handle greater thermal loads.
By properly managing heat generation and dissipation, power supply designers can optimize and increase efficiency, improve reliability, and extend product lifetimes. With decades of experience in electronics thermal management, Acton can provide quality TIM solutions tailored for your specific power supply needs.
Thermal Interface Materials for Managing Heat

When designing power supplies, thermal management is crucial. As components become more powerful, they also generate more heat. If this heat is not properly dissipated, it can damage sensitive electronics and reduce performance. Thermal interface materials (TIMs) play an important role in conducting heat away from components to heat sinks and cooling fans.
Choosing the Right TIM
There are several types of TIMs to choose from based on your needs:
- Thermal pads are flexible, compressible pads that conform to surface imperfections. They are inexpensive but less thermally conductive than greases or pastes.
- Thermal greases and pastes are viscous materials that can fill microscopic air pockets between surfaces. They are moderately priced and thermally conductive but require careful application and can be messy to use.
- Phase change materials start as a wax or grease but change to a solid form at operating temperatures. They require no cure time and conform well to surfaces but can be difficult to remove.
- Metal-based TIMs contain particles of thermally conductive metals like silver and provide the best thermal transfer. However, they tend to be expensive and abrasive.
For most power supply designs, a thermal grease or paste offers the best performance for the cost. Be sure to choose a formula that is chemically compatible with your components and heat sink materials. Apply the TIM in an even layer before assembling your power supply, and reapply if you notice higher operating temperatures over time.
Custom Solutions from Acton Technology
If you have a challenging thermal management problem in your power supply design, consider custom TIM solutions from Acton. We offer specialized thermal pads, greases, and other materials tailored to the exact needs of your application. Our experts can help determine the optimal solution based on factors like maximum operating temperature, component layout, and cost targets.
Electronic Components Distributor
Power Supply Design Solutions
Get reliable power supply design solutions with Acton Technology's customized electronic components and services in Singapore, Thailand, Philippines, Vietnam, and Malaysia. Benefit from rigorous testing, efficiency, and supply chain capabilities across Southeast Asia
Get Expert Advice





