E-MOBILITY
E-mobility, the latest “trend” in green recovery? or the revolutionary zenith of transportation? To answer this question, we must first have a rudimentary understanding of the technological powerhouse behind E-mobility. E-mobility, otherwise known as Electro Mobility is the collective use of electronic powertrain technologies, in-vehicle information, communication technologies and connected infrastructure, that allows for the electric propulsion of various transportation modes. In comparison with traditional modes of transportation such as motor vehicles, studies show that E-mobility significantly cut down on noise and carbon emissions as well as, minimize worldwide dependency on fossil fuels thus, offering global consumers a more economical option for fuel consumption. In an ever environmentally-conscious international economy, E-mobility is our future and just one of the many ways in which eco-savvy consumers are doing their part for our planet.
Electronic powertrain technologies in commercial transportation come in a variety of forms including battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. While fuel cell vehicles convert pure hydrogen gas into electricity in the fuel cell, BEVs and PHEVs require charging stations, also known as off-board chargers, and an on-board charger in the vehicle. Electric vehicles also have the alternative of wireless chargers however, wireless charging solutions are still in an early stage of development and face myriad obstacles that prevent it from being adopted as the mainstream charging solution for electric vehicles in the near future.
TRENDS
In recent years, despite the economic challenges of the chip shortage, Russo-Ukrainian War, and the ongoing Covid-19 Pandemic that has led to strict lockdown and prevention measures in China, electric vehicle sales have defied the odds and exhibited tremendous growth, owing largely to the sundry of EV models marketed as ‘miniature’ and ‘affordable’. Greater trials are still to come, however, in the form of increased cost pressures because of increasingly expensive power batteries, a direct effect of the Russo-Ukrainian war, and weakened demand from the withdrawal of car purchase subsidies in certain countries and worldwide inflation. Nevertheless, automakers are still expected to prioritise production of electric vehicles which will encourage continued growth of the electric vehicle industry, as well as derived demand for electronic micro components and automotive software that play a part in the fundamental structure of EVs and auxiliary equipment. This is supported by statistics indicating that the automotive software market would have grown by approximately 250 percent by the end of the decade.
CRITICAL FEATURES OF EV COMPONENTS
High Voltage
Higher voltage systems allow electric vehicles to use a lower current when charging its battery, reducing the potential of overheating and enabling more efficient power retention, which can be channeled towards increasing vehicle operational lifetime or travelling range.
Check out Yageo’s High Voltage Chip Resistor RV Series or Kemet’s Snap-In Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors ALA8A series for electronic components to use in a high voltage system
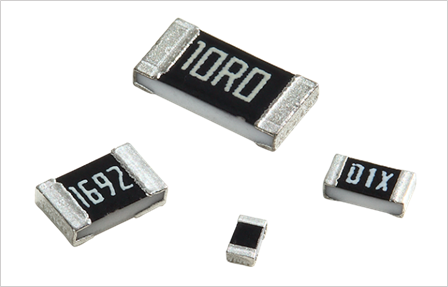
YAGEO HIGH VOLTAGE CHIP RESISTOR RV SERIES
| SPECIFICATIONS | FEATURES | APPLICATONS |
| AEC-Q200 qualified RoHS compliant | High component and equipment reliability | Converter |
| Sizes 0603/0805/1206/2010/2512 | Provide safety and reliability in discharge, balancing | Battery charger |
| Operating temperature range: –55 °C to +155 °C | Power supply | |
| IEC 62368-1:2018 for 0603 (100KΩ ~ 10MΩ) 0805 (100KΩ ~ 22MΩ) 1206 (100KΩ ~ 10MΩ) | Car electronics |
KEMET SNAP-IN ALUMINUM ELECTROLYTIC CAPACITORS ALA8A SERIES
| SPECIFICATIONS | FEATURES | APPLICATONS |
| AEC-Q200 qualified | Operational lifetime of 2,000 hours at +105°C | On-board chargers |
| Vibration proof 10 g | High ripple current | Inverters |
| Capacitance Range 120 – 680 µF | Excellent surge voltage capability | Wall Boxes |
| Rated Voltage 400 – 500 VDC |
IN VEHICLE SAFETY
Electric vehicles, by their very nature, present several unique hazards not found in traditional vehicles with internal combustion engines; most commonly, electrical, chemical, and thermal hazards. An example would be the use of sodium-sulfur batteries in EVs, sodium and sulfur are both highly reactive elements that have the potential to generate, via a variety of reactions, large quantities of heat, explosive and toxic gases, and other caustic compounds in the case of an unintentional collision. As a result, preventative or cautionary measures specific to internal design is necessary.
Featuring Yageo’s Automotive Grade Thin Film Chip Resistor AT Series and its superior resistance against sulfur-containing environments:
YAGEO AUTOMOTIVE GRADE THIN FILM CHIP RESISTOR AT SERIES:
| SPECIFICATIONS | FEATURES | APPLICATONS |
| AEC-Q200 qualified | Superior resistance against sulfur containing atmosphere | Automotive electronics |
| sizes 0402/0603/0805/1206 | Halogen Free Epoxy | Industrial and medical equipment |
| Operating temperature range: –55 °C to +155 °C | Total lead free | Test and measuring equipment |
| Telecommunications |
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS SUCH AS TEMPERATURE, HUMIDITY
Temperature affects the rate and efficiency at which chemical reactions occur inside a battery, this in turn can have a positive or negative impact on the operational lifetime or charging duration of an EV battery. Likewise, as batteries in EVs are actively cooled by air or water to prevent battery overheating during vehicular operation, an environment high in humidity levels could lead to the accumulation of moisture in the battery, increasing the risk of a short-circuit, resulting in damage to the battery.
Featuring Kemet Polymer Tantalum T598 series with Improved capacitance retention at high frequencies:
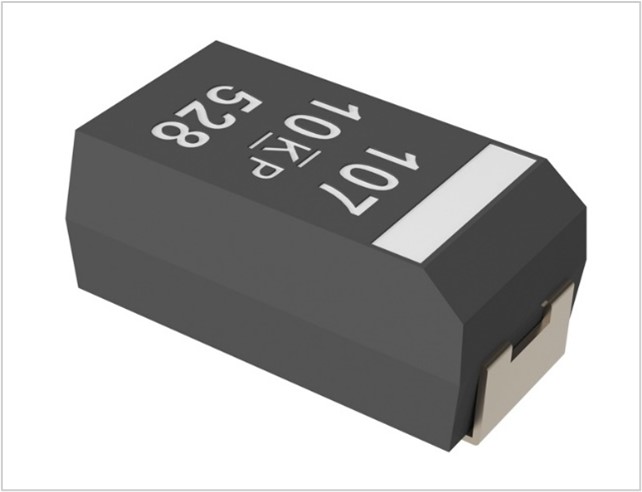
KEMET HIGH HUMIDITY AND HIGH TEMPERATURE POLYMER TANTALUM T598 SERIES
| SPECIFICATIONS | FEATURES | APPLICATONS |
| AEC-Q200 qualified | Ultra low ESR | Automotive (infotainment, ADAS, chassis and safety, Powertrain) |
| Rated Capacitance Range 4.7 – 470 µF at 120 Hz/25°C | Improved capacitance retention at high frequencies | |
| Operating Temperature −55°C to 105°C/125°C/150°C | ||
| Rated Voltage Range 2.5 – 75 V |
PULSE EV CHARGING SOLUTIONS
Level 3 EV Chargers require multiple communication protocols to monitor operation, report incidents, billing and to interface with customers. Pulse is able to offer a range of standard or customised products for both wired or wireless communication protocol.
| Communication protocols | Pulse Products |
| Wired Communication | ICM & Discrete Ethernet, PLC, CMCs, RF Inductors |
| Communication protocols | Pulse Products |
Wireless Communication | NFC, Embedded/Internal/External Antennas |
Finding the best product for your specific requirement isn’t always clear-cut.
Get in touch from us to find out in details what solutions we have for you!